Ultrafast dissipative soliton generation in anomalous dispersion achieving high peak power beyond the limitation of cubic nonlinearity
doi: 10.1186/s43074-023-00112-5
Ultrafast dissipative soliton generation in anomalous dispersion achieving high peak power beyond the limitation of cubic nonlinearity
-
摘要:
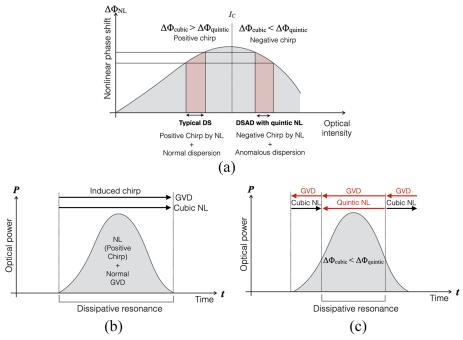
The maximum peak power of ultrafast mode-locked lasers has been limited by cubic nonlinearity, which collapses the mode-locked pulses and consequently leads to noisy operation or satellite pulses. In this paper, we propose a concept to achieve mode-locked pulses with high peak power beyond the limitation of cubic nonlinearity with the help of dissipative resonance between quintic nonlinear phase shifts and anomalous group velocity dispersion. We first conducted a numerical study to investigate the existence of high peak power ultrafast dissipative solitons in a fiber cavity with anomalous group velocity dispersion (U-DSAD) and found four unique characteristics. We then built long cavity ultrafast thulium-doped fiber lasers and verified that the properties of the generated mode-locked pulses match well with the U-DSAD characteristics found in the numerical study. The best-performing laser generated a peak power of 330 kW and a maximum pulse energy of 80 nJ with a pulse duration of 249 fs at a repetition rate of 428 kHz. Such a high peak power exceeds that of any previous mode-locked pulses generated from a single-mode fiber laser without post-treatment. We anticipate that the means to overcome cubic nonlinearity presented in this paper can give insight in various optical fields dealing with nonlinearity to find solutions beyond the inherent limitations.
Abstract: The maximum peak power of ultrafast mode-locked lasers has been limited by cubic nonlinearity, which collapses the mode-locked pulses and consequently leads to noisy operation or satellite pulses. In this paper, we propose a concept to achieve mode-locked pulses with high peak power beyond the limitation of cubic nonlinearity with the help of dissipative resonance between quintic nonlinear phase shifts and anomalous group velocity dispersion. We first conducted a numerical study to investigate the existence of high peak power ultrafast dissipative solitons in a fiber cavity with anomalous group velocity dispersion (U-DSAD) and found four unique characteristics. We then built long cavity ultrafast thulium-doped fiber lasers and verified that the properties of the generated mode-locked pulses match well with the U-DSAD characteristics found in the numerical study. The best-performing laser generated a peak power of 330 kW and a maximum pulse energy of 80 nJ with a pulse duration of 249 fs at a repetition rate of 428 kHz. Such a high peak power exceeds that of any previous mode-locked pulses generated from a single-mode fiber laser without post-treatment. We anticipate that the means to overcome cubic nonlinearity presented in this paper can give insight in various optical fields dealing with nonlinearity to find solutions beyond the inherent limitations. -
[1] Shi H, et al. Review of low timing jitter mode-locked fiber lasers and applications in dual-comb absolute distance measurement. Nanotechnol Precis Eng. 2018;1:205–17. [2] Jang Y-S, Kim S-W. Distance measurements using mode-locked lasers: a review. Nanomanuf Metrol. 2018;1:131–47. [3] Vyhlídal D, Jelínek M, Čech M, Kubeček V. Performance evaluation of fast, high precision laser rangefinder electronics with a pulsed laser. Proc Spie. 2011;8306:83060D-1–7. [4] Lee J, Kim Y-J, Lee K, Lee S, Kim S-W. Time-of-flight measurement with femtosecond light pulses. Nat Photonics. 2010;4:716–20. [5] Soltanian R, Long P, Goher QS, Légaré F. All-fiber sub-20 ps ultra low repetition rate high peak power mode-locked fiber laser to generate supercontinuum. Laser Phys Lett. 2020;17:025104. [6] Alani IAM, Lokman MQ, Ahmed MHM, Al-Masoodi AHH, Latiff AA, Harun SW. A few-picosecond and high-peak-power passively mode-locked erbium-doped fibre laser based on zinc oxide polyvinyl alcohol film saturable absorber. Laser Phys. 2018;28:075105. [7] Rudy CW, Digonnet MJF, Byer RL. Advances in 2-μm Tm-doped mode-locked fiber lasers. Opt Fiber Technol. 2014;20:642–9. [8] Cai J-H, Chen S-P, Hou J. 11-kW peak-power dissipative soliton resonance in a mode-locked Yb-fiber laser. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett. 2017;29:2191–4. [9] Bale BG, Boscolo S, Kutz JN, Turitsyn SK. Intracavity dynamics in high-power mode-locked fiber lasers. Phys Rev A. 2010;81:033828. [10] Li J, et al. All-fiber passively mode-locked Tm-doped NOLM-based oscillator operating at 2-μm in both soliton and noisy-pulse regimes. Opt Express. 2014;22:7875–82. [11] Wang X, Zhou P, Wang X, Xiao H, Liu Z. Pulse bundles and passive harmonic mode-locked pulses in Tm-doped fiber laser based on nonlinear polarization rotation. Opt Express. 2014;22:6147–53. [12] Smirnov S, Kobtsev S, Kukarin S, Ivanenko A. Three key regimes of single pulse generation per round trip of all-normal-dispersion fiber lasers mode-locked with nonlinear polarization rotation. Opt Express. 2012;20:27447–53. [13] Schibli TR, Thoen ER, Kärtner FX, Ippen EP. Suppression of Q-switched mode locking and break-up into multiple pulses by inverse saturable absorption. Appl Phys B. 2000;70:S41–9. [14] Broderick NGR, Offerhaus HL, Richardson DJ, Sammut RA. Power scaling in passively mode-locked large-mode area fiber lasers. IEEE Photonics Technol Lett. 1998;10:1718–20. [15] Broderick NGR, et al. Large mode area fibers for high power applications. Opt Fiber Technol. 1999;5:185–96. [16] Liu W, et al. Single-polarization large-mode-area fiber laser mode-locked with a nonlinear amplifying loop mirror. Opt Lett. 2018;43:2848–51. [17] Ding E, Lefrancois S, Kutz JN, Wise FW. Scaling fiber lasers to large mode area: an investigation of passive mode-locking using a multi-mode fiber. IEEE J Quantum Electron. 2011;47:597–606. [18] Li C, et al. Fiber chirped pulse amplification of a short wavelength mode-locked thulium-doped fiber laser. APL Photonics. 2017;2:1213021-5i. [19] Sobon G, et al. Chirped pulse amplification of a femtosecond Er-doped fiber laser mode-locked by a graphene saturable absorber. Laser Phys Lett. 2013;10:035104. [20] Sumimura K, Yoshida H, Fujita H, Nakatsuka M. Femtosecond mode-locked Yb fiber laser for single-mode fiber chirped pulse amplification system. Laser Phys. 2007;17:339–44. [21] Stock ML, Mourou G. Chirped pulse amplification in an erbium-doped fiber oscillator/ erbium-doped fiber amplifier system. Optics Commun. 1994;106:249–52. [22] Maine P, Strickland D, Bado P, Pessot M, Mourou G. Generation of ultrahigh peak power pulses by chirped pulse amplification. IEEE J Quantum Electron. 1988;24:398–403. [23] Galvanauskas A. Mode-scalable fiber-based chirped pulse amplification systems. IEEE J Sel Top Quantum Electron. 2001;7:504–17. [24] Huttunen A, Törmä P. Optimization of dual-core and microstructure fiber geometries for dispersion compensation and large mode area. Opt Express. 2005;13:627–35. [25] Yu-lai S, Wen-tao Z, Guoling L, Yuan T, Shan T. Optimal design of large mode area all-solid-fiber using a gray relational optimization technique. Optik. 2021;242:167188. [26] Li F, et al. A large dispersion-managed monolithic all-fiber chirped pulse amplification system for high-energy femtosecond laser generation. Opt Laser Technol. 2022;147:107684. [27] Fermann ME, Sugden K, Bennion I. High-power soliton fiber laser based on pulse width control with chirped fiber Bragg gratings. Opt Lett. 1995;20:172–4. [28] Cabasse A, Martel G, Oudar JL. High power dissipative soliton in an Erbium-doped fiber laser mode-locked with a high modulation depth saturable absorber mirror. Opt Express. 2009;17:9537–42. [29] Ding E, Grelu P, Kutz JN. Dissipative soliton resonance in a passively mode-locked fiber laser. Opt Lett. 2011;36:1146–8. [30] Chongyuan H, et al. Developing high energy dissipative soliton fiber lasers at 2 micron. Sci Rep-uk. 2015;5:13680. [31] Peng J, Boscolo S, Zhao Z, Zeng H. Breathing dissipative solitons in mode-locked fiber lasers. Sci Adv. 2019;5:eaax1110. [32] Chang W, Soto-Crespo JM, Ankiewicz A, Akhmediev N. Dissipative soliton resonances in the anomalous dispersion regime. Phys Rev A. 2009;79:33840–5. [33] Liu X. Coexistence of strong and weak pulses in a fiber laser with largely anomalous dispersion. Opt Express. 2011;19:5874. [34] Duan L, Liu X, Mao D, Wang L, Wang G. Experimental observation of dissipative soliton resonance in an anomalous-dispersion fiber laser. Opt Express. 2012;20:265. [35] Zhao J, Li L, Zhao L, Tang D, Shen D. Dissipative soliton resonances in a mode-locked holmium-doped fiber laser. IEEE Photonic Tech L. 2018;30:1699–702. [36] Krzempek K, Abramski K. Dissipative soliton resonance mode-locked double clad Er: Yb laser at different values of anomalous dispersion. Opt Express. 2016;24:22379. [37] Ibarra-Escamilla B, et al. Dissipative soliton resonance in a thulium-doped all-fiber laser operating at large anomalous dispersion regime. IEEE Photonics J. 2018;10:1–7. [38] Peng J, Zeng H. Soliton collision induced explosions in a mode-locked fibre laser. Commun Phys. 2019;2:34. [39] Zhou Y, Ren Y-X, Shi J, Wong KKY. Breathing dissipative soliton explosions in a bidirectional ultrafast fiber laser. Photon Res. 2020;8:1566–72. [40] Haus HA. Theory of mode locking with a fast saturable absorber. J Appl Phys. 1975;46:3049–58. [41] Haus HA, Fellow L. Mode-locking of lasers. Sel Top Quantum Electron. 2000;6:1173–85. [42] Haus H. Parameter ranges for CW passive mode locking. IEEE J Quantum Electron. 1976;12:169–76. [43] Liu X. Dissipative soliton evolution in ultra-large normal-cavity-dispersion fiber lasers. Opt Express. 2009;17:9549. [44] Liu X. Numerical and experimental investigation of dissipative solitons in passively mode-locked fiber lasers with large net-normal-dispersion and high nonlinearity. Opt Express. 2009;17:22401–16. [45] Liu D, Zhu X, Wang C, Yu J, Hu D. Low-repetition-rate, high-energy, twin-pulse, passively mode locked Yb3+-doped fiber laser. Appl Opt. 2011;50:484–91. [46] Zhang M, Chen L, Zhou C, Cai Y, Zhang Z. Ultra-low repetition rate all-normal-dispersion linear-cavity mode-locked fiber lasers. 2009. [47] Kobtsev S, Kukarin S, Fedotov Y. Ultra-low repetition rate mode-locked fiber laser with high-energy pulses. Opt Express. 2008;16:21936–41. [48] Liu XM, Mao D. Compact all-fiber high-energy fiber laser with sub-300-fs duration. Opt Express. 2010;18:8847–52. [49] Jeong H, et al. All-fiber Tm-doped soliton laser oscillator with 6 nJ pulse energy based on evanescent field interaction with monoloayer graphene saturable absorber. Opt Express. 2016;24:14152. [50] Choi SY, Jeong H, Hong BH, Rotermund F, Yeom D-I. All-fiber dissipative soliton laser with 10.2 nJ pulse energy using an evanescent field interaction with graphene saturable absorber. Laser Phys Lett. 2014;11:15101. [51] Zhu X, Wang C, Liu S, Zhang G. Tunable high-order harmonic mode-locking in Yb-doped fiber laser with all-normal dispersion. IEEE Photonics Technology Letters. 2012;24:754–6. [52] Wang J, et al. All-normal-dispersion passive harmonic mode-locking 220 fs ytterbium fiber laser. Appl Optics. 2014;53:5088. [53] Peng J, Zhan L, Luo S, Shen Q. Passive harmonic mode-locking of dissipative solitons in a normal-dispersion Er-doped fiber laser. J Lightwave Technol. 2013;31:3009–14. [54] Huang SS, et al. High order harmonic mode-locking in an all-normal-dispersion Yb-doped fiber laser with a graphene oxide saturable absorber. Laser Phys. 2013;24:015001. [55] Wu X, Tang DY, Zhang H, Zhao LM. Dissipative soliton resonance in an all-normaldispersion erbium-doped fiber laser. Opt Express. 2009;17:5580. [56] Choi SY, Jeong H, Hong BH, Rotermund F, Yeom D-I. All-fiber dissipative soliton laser with 10.2 nJ pulse energy using an evanescent field interaction with graphene saturable absorber. Laser Phys Lett. 2013;11:015101. [57] Semaan G, et al. 10 µJ dissipative soliton resonance square pulse in a dual amplifier figure-of-eight double-clad Er: Yb mode-locked fiber laser. Opt Lett. 2016;41:4767. [58] Zhang H, Bao Q, Tang D, Zhao L, Loh K. Large energy soliton erbium-doped fiber laser with a graphene-polymer composite mode locker. Appl Phys Lett. 2009;95:141103. [59] Engelbrecht M, Haxsen F, Ruehl A, Wandt D, Kracht D. Ultrafast thulium-doped fiber-oscillator with pulse energy of 4.3 nJ. Opt Lett. 2008;33:690–2. [60] Sayinc H, Mortag D, Wandt D, Neumann J, Kracht D. Sub-100 fs pulses from a low repetition rate Yb-doped fiber laser. Opt Express. 2009;17:5731–5. [61] Chen T, Liao C, Wang DN, Wang Y. Passively mode-locked fiber laser by using monolayer chemical vapor deposition of graphene on D-shaped fiber. Appl Opt. 2014;53:2828–32. [62] Chong A, Renninger WH, Wise FW. Route to the minimum pulse duration in normal-dispersion fiber lasers. Opt Lett. 2008;33:2638–40. [63] Zhang H, et al. Graphene mode locked, wavelength-tunable, dissipative soliton fiber laser. Appl Phys Lett. 2010;96:111112. [64] Rodriguez-Morales LA, et al. Long cavity ring fiber mode-locked laser with decreased net value of nonlinear polarization rotation. Opt Express. 2019;27:14030–40. [65] Chamorovskiy A, et al. Femtosecond mode-locked holmium fiber laser pumped by semiconductor disk laser. Opt Lett. 2012;37:1448–50. [66] Zhang H, Tang DY, Zhao LM, Bao QL, Loh KP. Large energy mode locking of an erbium-doped fiber laser with atomic layer graphene. Opt Express. 2009;17:17630–5. [67] Jung M, et al. Mode-locked pulse generation from an all-fiberized, Tm-Ho-codoped fiber laser incorporating a graphene oxide-deposited side-polished fiber. Opt Express. 2013;21:20062–72. [68] Kadel R, Washburn BR. Stretched-pulse and solitonic operation of an all-fiber thulium/holmium-doped fiber laser. Appl Opt. 2015;54:746–50. [69] Wan P, Yang L-M, Liu J. High pulse energy 2 µm femtosecond fiber laser. Opt Express. 2013;21:1798–803. [70] Song Y-W, Jang S-Y, Han W-S, Bae M-K. Graphene mode-lockers for fiber lasers functioned with evanescent field interaction. Appl Phys Lett. 2010;96:051122. [71] Junting L, et al. High output mode-locked laser empowered by defect regulation in 2D Bi2O2Se saturable absorber. Nat Commun. 2022;13:3855.








 下载:
下载: